Security is important when using mobile devices, especially when connecting to the Internet. Read on to find out what you need to know.
Security Challenges On Mobile Devices
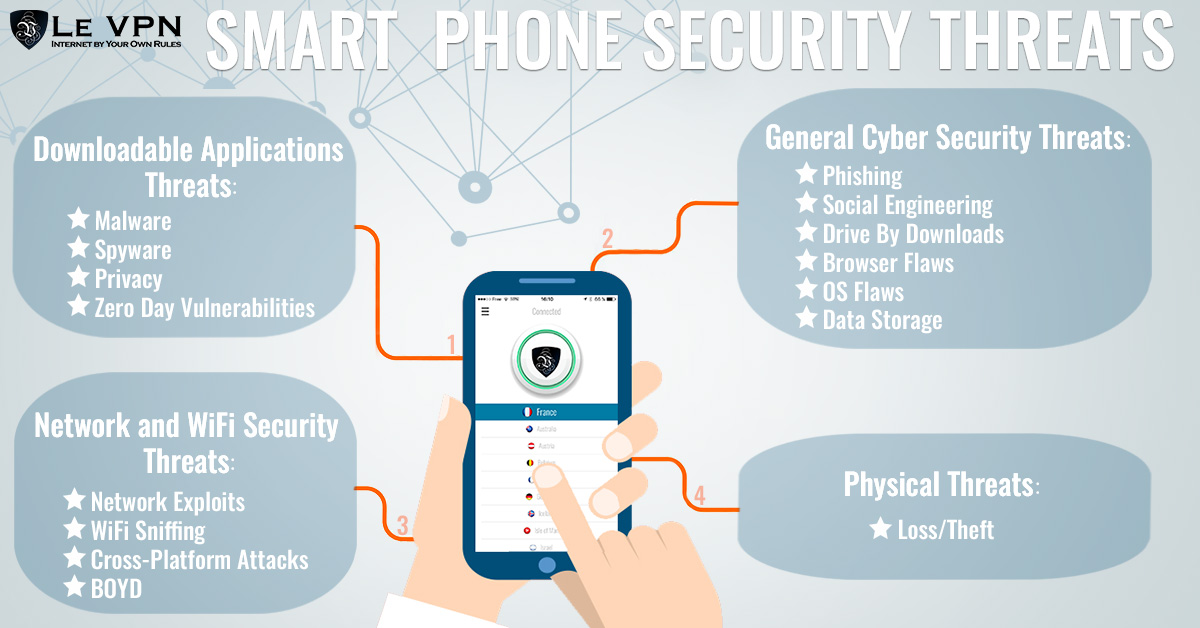
Believe it or not there are security risks when using a mobile device. I know, it’s surprising right, that your phone or tablet could be a possible threat to your safety. When you consider all the potential threats that exists on the Internet, and the fact that most of today’s mobile devices are connecting to and through the Internet with every function, I think it becomes easier to understand just how vulnerable they are. While many of the threats are the same as those faced by the average laptop or desktop user there are some unique to the mobile world. There are four basic types of threats mobile devices are susceptible to. Mobile phone security threats include application based, web based, network based and physical threats.
Smart Phone Security Threats
1. Downloadable applications threats
Downloadable applications pose the most common risk for mobile users; most devices don’t do much on their own, it’s the applications that make them so awesome and we all download apps. When it comes to apps the risks run from bugs and basic security risks on the low end of the scale all the way through malicious apps with no other purpose to commit cyber crime.
- Malware – malware is software that makes unwanted changes to your phone. This could include accessing email accounts, sending spam to your contacts or worse… give control of your phone to a third party. Ransomware is a growing trend among Internet scammers and is being used on mobile devices too. Malware locks your computer until you pay the ransom to get control back.
- Spyware – spyware is software that is intended to track or monitor devices and their users. It can collect any and all data and information stored on your phone, or transmitted through text, email or Internet.
- Privacy – privacy threats exists above and beyond the scope of intentional malware or spyware. All websites and applications collect some information about you, and that information is at risk of loss. Profiles on a chat site aren’t so much a problem but that changes when the info includes a government ID, bank account or sensitive password.
- Zero Day Vulnerabilities – Zero Day Vulnerabilities are flaws and potential points of entry within existing and otherwise trustworthy apps that have yet to be reported and/or fixed. Usually caused by poor coding or improper development these flaws and loopholes allow hackers, malware and spyware easy access to your devices and information.
2. General Cyber Security Threats
Due to the nature of mobile use, the fact that we have our devices with us everywhere we go and are connecting to the Internet while doing so, they face a number of unique web-based threats as well as the run-of-the-mill threats of general Internet use.
- Phishing Scams – Phishing scams can use your email, text messaging and even push notifications from social media to trick you into entering sensitive information. What makes them so hard to avoid is the sophisticated nature of the scams, many are impossible to distinguish from well know and trusted sites and often times all it takes is a simple click or like of a suggested page for malware to be downloaded to your device. Adding to the problem are small screen sizes and browsers that don’t display full URLs for links which makes it even easier to follow a bad one.
- Social Engineering is the latest buzzword in mobile attacks. These can range in degree but are aimed at using a person’s natural curiosity against them. One example is simply dropping a flash drive in a parking lot and waiting for someone to pick it up, and maybe look to see what’s on it. In some cases it may just be a lost drive, in others the drive could set to deliver malware into a device or network.
- Drive By Downloads – Some websites are set up to automatically download apps to your device whether you want it to or not. In most cases you will have to enable the app for it to work but this is not always the case. The apps could be innocent, and they could be malware or spyware.
- Browser Flaws – Some websites and applications can exploit flaws in your browser software or other programs used by it such as a Flash, PDF or media application. Visiting the wrong webpage can trigger an automatic exploit, just like a drive by.
- Operating System Flaws– The operating systems of mobile devices are a common point of attack as well as hackers seek new points of entry. Android powered devices are most at risk, they are the ones most often targeted by hackers, and fixed with patches and updates. Users of iOS are not immune though, attacks against that system have been growing at double digits for the past few years. Last year the NSO Group exploited a flaw in iOS to view emails, record sounds and track the movements of iPhone and iPad users. Earlier in the year a flaw in Linux coding put more than 1.4 billion Android users at risk of hijacking.
- Data Storage – We store a lot of data on our phones and that amount grows daily. Most phones utilize some form of encryption to protect your data but once a hacker gets past your security it doesn’t really matter.
3. Network and WiFi Security Threats
Mobile devices typically support a minimum of three network capabilities making them three-times vulnerable to network based attack. The networks often found on a mobile include cellular, WiFi and Bluetooth.
- Network exploits – no network is foolproof, there are flaws in the system, and they can be exploited for the purposes of downloading malware to your device. Bluetooth is especially vulnerable. Hackers can run programs to find any and all available Bluetooth connections within range and connect to them.
- WiFi sniffing – most websites do not use proper security when sending information across the web which makes it vulnerable to intercept. Mobile devices are constantly accessing this information across public WiFi networks which makes it easy to intercept. Black hats can easily scan the airwaves as they travel between your device and the WiFi access point, grab your data and steal it. They can also track the connections back to your devices and download malware, or mine your data.
- Cross-Platform Attacks – Hackers can deploy spyware to your computer which tracks data such as banking details. Once those are stolen a pop-up message suggests the Internet user download an app for “added security on your mobile device”, all you have to do is enter your phone number to get an SMS message with the download link. If done the hacker then has control of the laptop and the phone.
- BOYD – BOYD policies, bring your own devices, expose corporate networks to attack. Not only do the devices themselves pose risk as an entry point or Trojan Horse for malware, the infected devices can used to perpetrate complex phishing scams intended to unlock company information. Sophisticated hackers can send a purposefully infected device within the perimeter of a local WiFi enabled network and use that device to attack from within, avoiding firewalls and other security measures intended to protect from outside attack.
4. Physical Threats
Unlike a desktop sitting at your workstation, or even a laptop in your bag, a mobile device is subject to a number of everyday physical threats.
- Loss/Theft – Loss or theft is the most prevalent physical threat to the security of your mobile device. The device itself has value and can be sold on the secondary market, after all your information is stolen and sold.
How to Ensure Your Mobile Security and Privacy
Despite all these issues the number one threat to mobile security remains us, the users. To begin with, we are less likely to keep our operating systems up to date, which means we are not taking advantage of the latest security advancements. According to Symantec more than half of mobile users have no idea that security features even exist for mobile devices which is another big problem. Add to that the sharing and social nature of the Millennial generation and the opportunities for fraud and crime expand exponentially. As mobile devices improve and our use of them grows the number, types and quality of threat will grow too. Here are some tips on how to ensure your mobile security.
- Always password-protect your phone. Use passwords and if possible, fingerprint detection. This way if you forget your phone, lose it or it is stolen whoever finds it won’t have easy access.
- Only download safe apps. Apps are the easiest point of entry for hackers and malware because we willingly download them to our phone. All they have to do is make one attractive enough for us to want to download it. This is why it is important to get apps from trusted sources like the Google Play App Store or the iTunes App Store and even then it is important to verify an app’s trustworthiness by checking reviews from other users.
- Always read the terms and privacy policy. All apps collect and use our information to some extent. Always be sure to read the terms of use and privacy policy to see what information is collected, how it is used and where it may be shared.
- Turn off the Bluetooth. It is a good idea to turn off the Bluetooth on your mobile device when not using it. Aside from closing down a potential point of entry it will also cut down on your battery usage.
- Encrypt your phone. Most of today’s phones have some form of automatic encryption or encryption feature you can enable. Be sure to do so.
- Set up remote locate/wipe. Most phones have features that can be used to remotely wipe your phones memory and/or geolocate it. This feature is especially useful if there is sensitive data on your phone or you do not expect to get it back. When used in conjunction with password protection, it can keep the loss of data to a minimum.
- Back up your data. Most mobile users back up their data about as often as they update their operating systems, which is to say not too often. You can upload your phone’s settings, data, pictures, music and etc. to the cloud, which in itself poses a risk to your security, or directly to a laptop or PC.
- Don’t jailbreak or root your phone. The difference depends on whether your device is iOS or Android but the meaning is the same: you’ve bypassed manufacturer settings in order to use your phone in a way not originally intended. Doing this weakens your device’s natural security settings and exposes it to additional risks as well.
- Update the operating system. I know it’s a pain but it needs to be done. When you get the message that says a new OS is available, take the time to set it up and do the download.
- Download anti-malware. Yes, it does exist and you can get it from a number of sources. If you are using an Android device I highly recommend it.
- Use public WiFi with caution. Public WiFi is one of the many perks of using a mobile device, you can connect anywhere, it’s free and you can save on data minutes by using it. The downside is two-fold. First, the WiFi security – these connections are inherently insecure as they are open and available to anyone who wants to connect to them. This leads to the second problem which is that public WiFi connections attract black hats and hackers as a high-target environment. One way to protect yourself is with a VPN.
- Use a VPN. A VPN is a virtual private network. This technology uses software to encrypt your data before it leaves your device to travel across the WiFi network, and then sends it through a digital “tunnel” that is hard to detect and nearly impossible to track.
Challenges of Mobile VPN Use and the Best VPN Apps
VPNs are not new technology but have only recently been made available to the mobile market. These connections provide the highest level of security, privacy and anonymity available on the Internet today. While relatively easy to deploy on stationary devices such as desktops, routers or laptops that tend to sit in one place while connected, VPN is much more difficult to manually deploy on mobiles. Mobile devices are subject to rapid and frequent change in mode of connectivity and IP address as they move through real time, a mobile VPN must be able to adapt to that while maintaining integrity of connection.
The best VPN solution for your mobile security is installing and using a VPN app from a reliable and trustworthy VPN provider like Le VPN iPhone app. This VPN app allows you to encrypt and secure the connection of your mobile device with one single tap and no manual installation is required. You can easily pick any country that you wish to connect to and to save your favorite countries in the Favorites menu, or reconnect to your recent connections.
There are many benefits of VPN for your cell phone. They ensure a safe, secure and authenticated connection at all times and will alert you if the connection fails. This way you can guarantee your WiFi security in public hotspots ad be assured that no one is watching while you do your banking, pay a bill or check your baby monitor. In addition to this, your data and information is encrypted before leaving your device so that if it is intercepted for whatever reason, whoever finds it won’t be able to do anything it with it. Additionally, by connecting to a VPN network your IP address will always be masked which means that your phone could not be tracked or traced by malware or hackers.
Side benefits of using the VPN center around the fact your IP address is masked. The VPN network works because of dedicated VPN servers located around the world, each VPN provider has their own. When you log onto the network you choose a server located in a country of your choice and when connected you are given an IP address by that server, from the country in which it is located. This allows for things like unlocking geo-restricted content like US or UK television.
Le VPN is the leading provider of VPN for mobile and has solutions for both Android and iOS. The software can be downloaded directly to your phone and operated with the touch of a finger. Le VPN supports different protocols with varying level of securities intended for different purposes, including IKEv2, OpenVPN, L2TP over IPSec and PPTP. Once downloaded all you have to do is open the app, enter your user name/password, choose a server to connect to and the connection is made. A single account is good for multiple devices with 2 open connections at any one time and no limitations on bandwidth. The best part is that the service is very inexpensive at less than $5 per month.
Without doubt, mobile devices are here to stay. They are only going to get more complex with time and over time we will come to rely on them more and more. As the technology advances, so too will the threats. There will always be risk of vulnerabilities, so it is only right as a mobile user to take advantage of the latest cutting edge technology to protect yourself and that is Le VPN for mobile. Get Le VPN now and take its protection with you everywhere you go.
*Article Updated On October 5th, 2018.*
SUMMER SALE
First 3 years for $2.22/mo
NO LOGS
100+ LOCATIONS
P2P ALLOWED
Easy To Use
30-Day Money Back
Friendly Support
Bitcoin Accepted
Ultra High Speeds





Written by Vuk Mujović @VukMujovic
Vuk Mujović is the founder of MacTíre Consulting, an analyst, data management expert, and a long-term writer on all things business & tech. He authored blogs, articles, and opinion pieces aimed to help both companies and individuals achieve growth without compromising their security. Vuk is a regular guest author to Le VPN Blog since January 2018, where he gives his expert opinion on the topics related to cybersecurity, privacy, online freedom, and personal data protection. He also often shares his tips and best practices in relation to internet security and digital safety of private individuals and small businesses, including some additional applications of using a VPN service.
Comments (1)
how to solve forgotten pass word of admet fashion g6 mobile