For humans and computers alike, one of the main issues when talking about personal data protection is trust. Sadly, IP Spoofing is used to abuse the trust you and your devices have towards other members of your network and to damage either your connection or your equipment.
Usually, when talking about cybersecurity, you will hear about not opening emails from unknown sources or running programs from unfamiliar senders. This is all sound advice, but what happens when that virus was sent from a device you recognize? What if someone spoofed your bosses IP address and sent you a virus in an email?
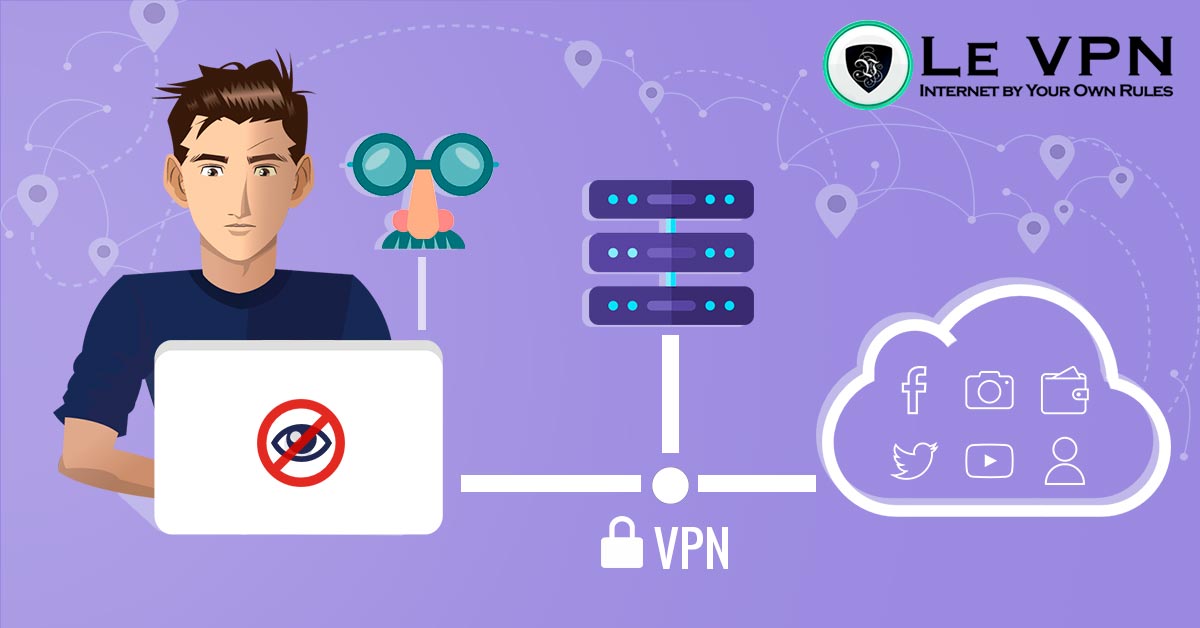
Thankfully, there are several ways to protect your device from IP spoofing. Regardless if you are a company or a private individual, you will want your general IP to be from a VPN and your true address to be hidden. Then, if you have a company, you can use a wide range of different tools to find out who is trying to hack you and to repel those attacks.
For individual users, it is best to use a premium VPN that already includes these services. Professional providers like Le VPN will do all of the legwork on their side so that you don’t need to establish your own defense systems at home.
What Is an IP Address?
Simply speaking, the IP address you would see if you ask Google is the address of your modem.
Going into more detail, it is actually the address logged into the header of the data package that you are sending. When using the internet unprotected it will be your home modem, but if you are using a VPN it will be the address of the provider, and the server you are connecting over.
Similar to how your VPN provider changes your IP address for the websites you are visiting, hackers can modulate their own files to have some other IP address in the header.
In most cases, they will not know which is the address of a device that you might trust, but if they can compromise a device, they will be able to use the IP of that device to trick your computer and security systems. Thus, if they enter a company system, every computer in that system is in danger.
Finally, the most common way of using IP spoofs is to create multiple dummy addresses and guide them all to do one simple task, like entering a website. This is how DDoS attacks are made, or how someone could establish a LOIC.
IP Spoofing Is not Always Bad
There are a few good reasons why companies and even some individuals would want to have software capable of spoofing IP addresses. It is the old saying: ‘’Know thy enemy.’’
Generally, many DDoS attacks that are performed are actually planned, as they are used to test the resilience of a website or service or to gauge the network capacity. Both systems are akin to vaccinating the system before it encounters a real attack.
If you want to have a good website, you will need to know if your hosting service can protect you from malicious attacks such as denial of service attacks.
Finally, using spoofed IP addresses, developers test their own systems and if it would be able to sniff out and find whoever the attacker is.
Malicious Spoofing
While many attacks that use IP spoofing are not malicious, we should be more concerned about those that are.
Unlike the past where hacking was mostly a matter of honor between computer enthusiasts and self-proclaimed anarchists, now it is mainly for personal gain. This might seem to exclude most private individuals, but in all actuality, most money is in private accounts. Personal data is a huge source of income for cybercrime organisations around the world.
As we have mentioned, in most cases the culprits will not know which IP address to spoof and would use this sort of attack to crash websites. This can be quite problematic for companies that have online shops as they will lose not only the revenue, but also the trust of their customers. This type of attack can be the idea of the hacker, as they plan to hold the website for ransom. Also, it can be financed by a competitor that wants to gain an edge.
In the case where the hacker, or however the sender want’s to call themselves, knows the exact IP the situation becomes quite a bit trickier.
Unless you are using a professional VPN provider like Le VPN, that will hide all traces of your modem’s IP address, there is a good chance that the hacker will be able to trick either your device or you personally. You will need to be vigilant and never open weird looking files.
Who Is the Usual Culprit?
Culprits of IP spoofing can be segregated into three distinct categories:
- The Competitor
- The Syndicate
- The Insider
While these three groups might sometimes work together for a single malicious purpose, they generally have different approaches and different tools to work with. The most dangerous situation is when all three groups are working against one enemy, usually a company, and that is the most common example of corporate espionage today.
The Competitor
As mentioned, they are your adversary. While we don’t exclude the possibility of someone having a personal nemesis, this is usually done in business settings. The competitor will pay people to run DDoS attacks and try to bring down a website or a system, damaging the revenue of another company.
The Syndicate
Regrettably, the name that used to mean a worker’s collective has been hijacked by many criminal organizations that would like to romanticize the fact that they are criminals. These organizations will hold websites, systems, and content for ransom and especially love having personal data.
Unlike the competitor, which is primarily a business, this is a criminal enterprise, meaning that there is no such thing as ‘’too small’’ for them.
The Insider
The smallest, and yet the most dangerous type. The insider is the person who has access to your IP address and to a device that you trust.
It should be noted that most insiders don’t know that they are insiders, as they just didn’t report their device or passwords being stolen. Also, these devices could have been cloned, making them an unknowing accomplice.
Company Hardware Hacking
While most people don’t care about what happens to companies, especially the large ones that we know don’t care about us, it is important to be aware of the process. The main reason for understanding the way hackers compromise companies is because there is a large chance that we are a cog in that chain that we can become compromised ourselves.
Primarily, the hacker will need access to the system. This may happen just by guessing the DHCP server IP or some of the company passwords but is usually done by stealing devices or tricking employees. They will then start changing the header in their data packets so that their source address resembles that of a trusted device.
Next, they will send out a ‘’phishing attack”. In most cases, they will not know who owns the source address that they are spoofing and will be phishing blind. They will try to send IP packets to as many addresses as they can find in the server hoping that someone will open.
In some cases, the subject of the message will be empty, and there will only be a single file inside, called something like ‘’Quarterly Report”. This is why it should be a protocol for emails to be adequately explained every time.
Trickle-down Insecurity
The reason why we should be aware of the ways hackers compromise companies is that most of us use private devices for work emails as well. This may be your laptop, or your smartphone, where you will open the malicious email and bring your work problems home.
Now there is a different problem, as all of your home devices will have authentication protocols with the phone, laptop, or tablet you brought to work or received work emails on.
Finally, if the server of your workplace has been compromised, you can even download malicious software through a browser when entering your company website.
Hacking Private Devices
Hacking personal devices is much harder than attacking companies. First of all, the hacker rarely knows who you are, or where you are. Also, they don’t know which IP addresses will pass your packet filtering, or if you will be able to detect that they are spoofing the address.
To hack an individual, hackers will use multiple sources. They will first try to steal some private information from a company that has your IP address on file and with which you already have device trust relationships.
Then, they will spoof that company’s information to try to trick your devices into accepting the message, finally getting to your private data.
How Can We Defend Ourselves?
Defending ourselves against scammers that use IP spoofing is actually quite easy as current personal data protection protocols predict that they will happen at some point.
If you are a business owner or have a website for any reason, you will need to set up some defenses that will prevent hackers from damaging your system. Currently, there is a wide range of IP filtering, as well as DNC registry databases that can be used to cripple any spoofing attack.
Otherwise, if you want to protect your own devices from such an attack, the simplest way to do so is to have a premium VPN provider that will include this in their service. Professional companies like Le VPN will have a whole host of protocols in place that will not only repel spoofing attack but will not lose any internet speed while doing so.
The important thing here is to know the difference between using a premium anonymous proxy from a VPN and using just a regular proxy connection from another server, which could have less security than you have on it.
Government Regulation
For the century and a half that the Massachusetts Institute of Technology is open, there was never a textbook as dry as are the laws concerning the internet. It is obvious that most writers of the law know very little on how the network operates and the protections established usually only inform the legitimate companies and institutions, like healthcare personnel or government officials, doing nothing for those who use the internet for malicious purposes.
If there is anything you should take from the GDPR, the DPA, and other national legislation is that you should not rely on the government for your cybersecurity. The GDPR will protect you from corporations, which is nice, but that shouldn’t be your last line of defense.
Data Protection Law of 2018
This law references the UK’s implementation of the GDPR. While this piece of legislation, combines with the Communications Act, has a wide range of flaws, including possibly severe infractions on free speech and civil rights, it does prevent the trickle-down effect we have mentioned earlier.
Personal Data Protection Act 2012
The Personal Data Protection Act of 2012, or PDPA for short, is a law in Singapore that guides how companies and individuals can collect and hold personal data. Generally, it didn’t come to as much criticism as its European counterparts.
In theory, this law should prevent companies from holding your private data on file without your consent or disclosing this information to others. The ones holding the data can only share relevant data that is allowed by the law and at strictly stated times. This is supervised by the Personal Data Protection Commission, or the PDPC.
The application of this law means that if the police catch someone with personal information, even if they have not (yet) committed another crime, they can be charged and the personal information deleted from their databases.
This law has been shown in action in January 2019 when a member of the healthcare personnel in Singapore leaked patient records that were stored in the NEHR database. Since then, access to the system information has been significantly reduced.
General Data Protection Regulation
The General Data Protection Regulation was brought by the European Commission and is the current set of data protection rules for the European Union.
While the GDPR should impact only EU citizens and companies, as most tech companies operate on the continent the rule has affected most of the global user population.
The GDPR dictates how companies, institutions, and governments can store personal information of any sort. This law also includes holding IP addresses that are connected to personal names or other personal information.
The result of this law is that by spoofing one device, even from a large company, hackers are unlikely to find personal information from other people.
Personal Data Protection Policy
Whenever you are asked to give any of your private information to a company you should ask for their Personal Data Protection Policy, or PDPP. By EU law, as well as most national laws, the company needs to have a devised strategy on how they will protect the data you will give them.
Once you have the personal data protection statement from the other side, try to find if there is something strange that you wouldn’t agree with. Anything like strange disclaimers how they are not at fault if they get hacked is a major red flag, and you should stay anonymous with that company.
Protecting All Devices
If you are using a premium VPN, the device connected through that server will be protected from an IP spoofing attack. But, often we forget that we do a lot of our browsing through our smartphones, as well as use consoles and other entertainment systems to stream videos online.
Devices that are not using a VPN are still at risk, and infecting one device in your home system means putting all of the computers on that network at risk.
Le VPN is a good choice here because you can not only install a VPN to all of the mobile devices that will leave home at some point but can also have a VPN router that will protect all of the devices in your home, including any IoT machines that you might have.
Advantages of a VPN
It looks like the answers to the questions of should I use a VPN are just stacking atop of each other. Aside from security and anonymity, which are the prime reasons why everyone should be using a VPN, there are now many others that are a welcomed bonus.
From access to worldwide content to a steadier connection, all the way to making multiplayer games on your console. It gives you the advantage of being at two places at once, at least digitally.
Peer-2-Peer Encryption
Something that has become a staple of premium VPN providers is P2P encryption, which is impervious to spoofing attacks.
While a hacker can simulate the IP of a trusted device, they don’t have their private encryption key, making it impossible to crack your code and fool your device. Mostly because of this type of encryption the IP spoof attack has been rarely used directly for some time, unless for DDoS attacks.
Conclusion
While IP spoofing is the favorite tool of scammers around the world, if you are using a premium VPN it will look like a silly thing to be afraid of. Professional VPN providers like Le VPN have a range of defenses against it, and such attacks can’t breach their protocols.
Finally, while the laws made by governments might not protect us from such attacks directly, they do help reduce the possibility of devices falling down like dominos. Hopefully, less and less companies and institutions will have our personal information in the future, and we will be able to browse the internet freely and without fear of scams and identity theft.
SUMMER SALE
First 3 years for $2.22/mo
NO LOGS
100+ LOCATIONS
P2P ALLOWED
Easy To Use
30-Day Money Back
Friendly Support
Bitcoin Accepted
Ultra High Speeds



Written by Vuk Mujović @VukMujovic
Vuk Mujović is the founder of MacTíre Consulting, an analyst, data management expert, and a long-term writer on all things business & tech. He authored blogs, articles, and opinion pieces aimed to help both companies and individuals achieve growth without compromising their security. Vuk is a regular guest author to Le VPN Blog since January 2018, where he gives his expert opinion on the topics related to cybersecurity, privacy, online freedom, and personal data protection. He also often shares his tips and best practices in relation to internet security and digital safety of private individuals and small businesses, including some additional applications of using a VPN service.