What are the countries with the fastest Internet speeds? Why do some countries have slower Internet speeds than others? The Internet is the same everywhere, right? Yes and No. The Internet and Internet speeds are not the same in every country.
Do All Countries Have Access To The Internet?
Yes indeed, all countries have access to the Internet. The trouble is that not all countries view the Internet the same, they don’t all have the same level of infrastructure or advancement in technology. What factors affect Internet speed depend on where you are, where you are connecting to and the number and types of networks that connection must pass through between here and there. Reduced down to the basic facts though there are two predominant factors affecting speed; money and expertise. On the side of the ISPs it comes down to how much money they spend on bandwidth and infrastructure, and on the expertise of the organization. On the side of the users it is much the same; how much money we spend on high performance equipment, and having the knowledge to use it.
Why Do Some Countries Have Slow Internet?
There are many reasons why one country may have slower Internet than another. These include things like the type of network the connections are made through as well as controls put on the net by government. Countries with the fastest Internet boast high levels of individual freedom as well as the most advanced technologies. Countries with the slowest Internet speeds are often those with the least amount of infrastructure and the most restrictions on personal freedoms.
- The quality of the exchange equipment makes a huge difference.
If they are using the old style DSLAMs speed could be as low as 7 mbs. Fiber optic connection would increase that to 50, 100 or even 1000 mbs.
- The amount of bandwidth provided.
Bandwidth is the amount of data that can be streamed at a given time. The more bandwidth, the more data and the faster your connections and downloads. In terms of ISPs and how they function, bandwidth is their single largest cost and the only means they have of controlling your use of the net. If they think you are using too much, or if they don’t like the source/type of data that you are accessing they can throttle your connections. Internet throttling or Internet filtering is the practice of intentionally slowing down connection speeds by reducing the amount of available bandwidth, among other techniques.
- Technical competence of the network providers.
Believe it or not, not all phone companies are the same and when it comes to the Internet those are the people operating the networks you use to access the World Wide Web. They may have the leading, state of the art cutting edge technology but without the savvy or experience to use it, and maintain it, properly connections speeds can be reduced dramatically. If you combine a less experienced crew with low-end technology, the chances of attaining optimum speeds are virtually impossible.
- The quality of the line, and I am not talking about the level of technology.
Here I am referring more to the quality of the equipment rather than its level of development. Sure, a fiber optic line is preferable to a copper one but only if the quality of the fiber optics provides a better connection speed than that of the copper. A high-grade copper wire may give better performance than a low grade fiber optic one. Most networks use a combination of copper and fiber, choosing the fiber for main-line connections and using copper to complete connections to the end user, home and office.
- Your equipment.
The equipment and settings you use to access the net can also have an impact on your connection speed. This includes your devices as well as the modems and routers provided by the ISP.
- Censorship /Government Control.
Censorship and government control can have a big effect on your Internet speeds regardless of your equipment and their infrastructure. Nations with low levels of control, high levels of personal freedoms and unimpeded access points will naturally have the higher speeds. Those that keep tight reign on the population and/or its access to the web will of course suffer slower connections.
The last mile is a phrase used in telecommunications to describe the last mile in the network. The final leg of connection to the home, business or end user. In today’s world it could mean the copper wires connecting your house to the telephone pole, the coaxial line powering your TV or the signal from the local cell tower. When it comes to connection speeds this is often the number 1 cause of bottlenecking. FTTH, fiber optic to the home, is the idea that high-speed broad band fiber optic connections can and should be used throughout the line, all the way to the local network and connections to the home.
Internet Speed, What Is a Fast Internet Speed
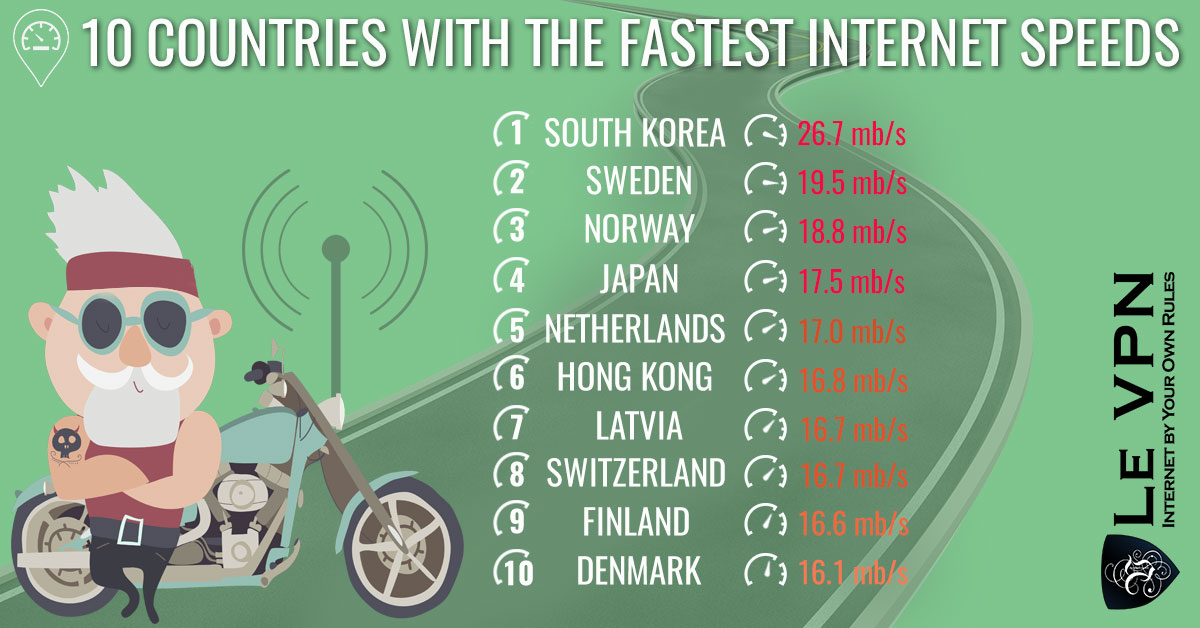
The global average Internet speed is about 5.5mb/s. This is fast enough to download an HD movie in about an hour. And that is considered to be “fast” Internet. Countries with average speeds below 4mb/s are considered to have slow speeds. Now, the fastest average speed in the world is South Korea at 26.7mb/s, fast enough to download that same movie in only a few minutes, as quick as 1 minute depending on the file size. Now consider that the average peak speed in South Korea, the fastest speed you could expect to have, is over 95mb/s and the time it takes to download an HD movie can be counted in seconds. Seconds. How long does it take you to download a movie?
What’s fascinating is the disparity between 1st and 2nd place and the rest of the field. There is a 7.5mb/s gap between the top two in terms of average speed but South Korea is much faster in terms of average peak. Where it averages peak speeds near 95mb/s and ranked 3rd globally Sweden is much slower at 69mb/s and not even a top ten nation. The disparity between 2nd place and 10th is much smaller, only 3mb/s with an average of 17.6mB/s, about 3X the global average. The US ranks about 14th with an average speed near 12.6mb/s.
Countries With The Fastest Internet Speeds Use Fiber Optics To The Home
Akamai maintains a listing of countries ranked by their Internet speeds. It is not surprising that many countries on this list are also countries with active and advanced technology sectors. What is surprising is that none of the top ten are what you might think of as the world’s leading nations, at least in terms of economic size, population, social development and other measures of society. What these nations do have in common are high levels of personal freedoms, and low levels of censorship and other impediments to Internet access. Believe it or not, the US is ranked 14th worldwide.
1. South Korea
South Korea is ranked #1 in terms of average connection speed and #3 in terms of average peak connection speed. Average speed is 26.7mb/s while average peak is a much higher 95.3mb/s. The nation has an Internet use rate near 95% of the population that is supported by wide sweeping governmental support of broadband and broadband technology. Along with this is a very high population density which connecting them all much easier than other places. Visitors to South Korea will be pleased to discover 3G connections over 95% of the country including inside subways, tunnels and buildings. They will also discover free public WiFi with similar coverage.
2. Sweden
Sweden comes in a distant 2nd in terms of average connection speeds. The average speed is just 19.5mb/s, about 27% slower than South Korea. The average peak speed is much slower than South Korea, not even ranked in the top 10. In terms of use, Sweden ranks 4th with 94% of the population connected in some way. According to the Open Net Initiative there is little to no censorship or government interference with the Internet. They do allow some monitoring of cross border traffic and implement filters to weed out child pornography. The constitution of Sweden protects the freedom of speech and the press, and prevents arbitrary interference with privacy, family, home and correspondence.
3. Norway
Norway s ranked 3rd in terms of average Internet connection speeds at 18.8mb/s. It boasts being the 1st non-English speaking nation on the net, having connected with the ARPANET in 1971 to help monitor communist Russia. Since then they have been a leader in building fiber optic and 4G infrastructure. Even remote islands in the far north have speeds far faster than most other countries. Norway’s constitution also protects the rights to privacy and freedoms of press and speech. The Open Net Initiative says there is no evidence of governmental filtering.
4. Japan
Japan is ranked 4th with average speeds near 17.5mb/s and 5th with peak average speeds near 82.5mb/s. In terms of roll out, Japan is among the first to fully realize the potential of the Internet and invest in its infrastructure. Japan is a leader in FTTH, fiber optics to the max, and has been using it for 100% of their networking needs. Major telecom providers offered ISP services as early as 1996 with the implementation of high-speed broadband in 2000. It is estimated that 86% of households and 99% of businesses larger than 100 employees use the net. In terms of regulation Japan’s Internet is among the least regulated, relying on a system of self-regulation implemented by the businesses that operate across the web. The country also protects the freedom of speech and the press with little to no limit on access or use of the net.
5. The Netherlands
The Netherlands is ranked 5th for average speed, 17.0mb/s. According to the OECD the Netherlands ties Switzerland in having the most broadband subscriptions per 100 inhabitants. It also boasts no broadband caps (limits on the amount of data that can be transmitted) and the most homes with 50mb/s+ connected homes in Europe. This is due to a nationwide roll out of fiber optic networking and the local loop bundling. The local loop allows for multiple access routes at the user end providing greater capability and redundancy in the case of damage or attack. The government actively supports no censorship or blocking of the net but does attempt to control copyright infringements, child pornography and other criminal uses.
6. Hong Kong
Hong Kong ranks 6th in terms of average speed but 2nd in terms of average peak speed. Average speed is 16.8mb/s, about average among top nations, but average peak is closer to 105mb/s, fast enough to download a lengthy movie in its entirety in minutes. Hong Kong shares a characteristic with South Korea having an incredibly large and unbelievably dense population, a characteristic that makes it incredibly easy to connect them all together. If Hong Kong has a problem with the net, it is that there is too much of it. This is because of aggressive use of FTTH and low pricing driven by high competition among ISPs.
7. Latvia
Latvia comes in 7th with an average speed near 16.7mb/s. The country has little to no censorship of the Internet, does not block access and employs fiber optics in an efficient manner. Travelers will be happy to find 3G and broadband connections just about every place they go and much of it is free. Further, Latvia is among a block of nations within central Europe well known for its history in mathematics. School children are introduced to math and technology and a young age and use it daily in the home and school.
8. Switzerland
Switzerland ties Latvia with average speeds near 16.7mb/s. The country has one of the highest Internet use penetration rates in Europe and is actively upgrading its networks. DSL and broadband over the phone are the number one means of access due to the high cost of fiber optics. Fiber optics are available but used primarily by business. The net has little to no limits on use although the Swiss will censor on a case-by-case basis. Freedom of the press and speech are protected but there are penalties for inflaming or provoking racial hatred or other criminal activities.
9. Finland
Finland is 9th in terms of average speed at 16.6mb/s. While its speeds may not match that of the fastest nations Finland does lead in two areas. It was one of the first countries to adopt widespread and mainstream use of the net, beginning in the early ’80’s, and is the first to make Internet access a national right. The country makes widespread use of fiber optic networking with FTTH available in many places. Finland also maintains freedom of the press and speech with no censorship or government impediments to access. Fees are usually low due to high competition with services offered in a variety of packages.
10. Denmark
Denmark rounds out the top 10 with an average connection speed of 16.1mb/s. While low compared to South Korea’s 27.6 it is still fast and 3 times the global average. What sets Denmark apart from most other nations with high connection speeds is the long running monopoly on telecommunications and the last-mile infrastructure. TDC, a formerly state owned monopoly, owns all the copper connections running into homes and businesses. Even so Danes enjoy low cost, high speed and reliable access above and beyond the average European. In recent years this monopoly has come under attack as private business consortiums begin to build out FTTH networks.
How a VPN Can Help Speed Up Your Connection
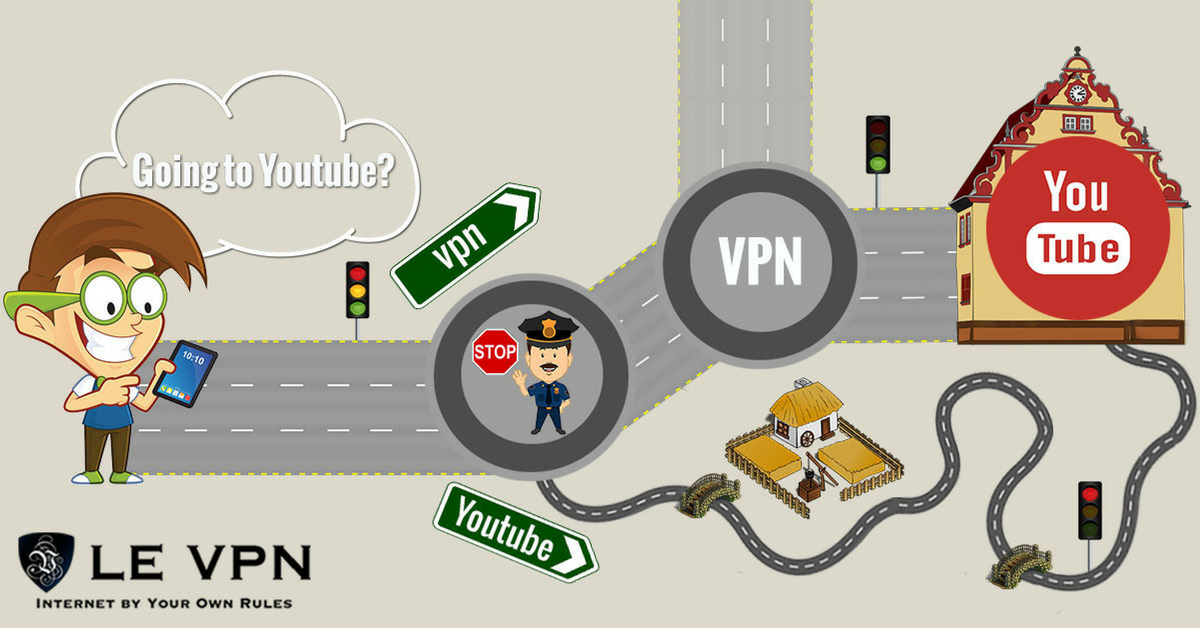
How can I speed up my Internet connection? Assuming you have already purchased the fastest connection you can get, have the best equipment you can afford and are using the Internet in an optimal fashion there is still one thing you can try. A VPN.
1. Censors /Throttling /Nefarious Influences.
Sometimes the reason you have slow Internet is because someone is watching you. This could be a censor, your ISP could be throttling/packet-shaping you, the network may be experiencing bottlenecks, whatever. The VPN can bypass all that and free up your connection speed. The VPN uses a system of dedicated servers that bypass local ISPs in favor of secure, unfettered access. The best VPNs like Le VPN provide completely unimpeded access and unlimited bandwidth.
2. The Local Network Sucks.
Let’s face it, not everybody has access to fiber optics and if they do – it doesn’t mean the last mile is fiber. Eve if the network around your home/office is the ultimate best, it can be that doesn’t mean the last mile to the website/network you are trying to access is the same, or that all the lines between here and there are either. If you are having trouble making a connection with a specific website or country you can try to use a VPN, either with a server in your own country or one in the target nation. The VPN network route is not the same as the public route and likely of higher quality and/or integrity.
3. Downloading Large Files/HD Movies/Streaming Media.
Even in the freest nations you can run into data caps and bandwidth limitations that can be avoided with a VPN. To make downloads even faster you can use a SmartDNS proxy with VPN which fortunately, Le VPN has ready to go.
The bottom line is simple. Not everyone gets the fastest Internet and that is a shame. The good news is that there are things you can do to mitigate that, and one of them is VPN. Yes, VPNs are for security and for unlocking geo-restricted content but they can also help speed up your connections. Even if they don’t, a good VPN will keep your computer safe and allow you to watch whatever content you’d like, so why not try it? There is a new hack announced every day, we’re not safe on the Internet so get Le VPN now.
*Article Updated On November 28th, 2018.*
SPRING SALE
GET 3 YEARS FOR $79.99
NO LOGS
100+ LOCATIONS
P2P ALLOWED
Easy To Use
30-Day Money Back
Friendly Support
Bitcoin Accepted
Ultra High Speeds




Written by Vuk Mujović @VukMujovic
Vuk Mujović is the founder of MacTíre Consulting, an analyst, data management expert, and a long-term writer on all things business & tech. He authored blogs, articles, and opinion pieces aimed to help both companies and individuals achieve growth without compromising their security. Vuk is a regular guest author to Le VPN Blog since January 2018, where he gives his expert opinion on the topics related to cybersecurity, privacy, online freedom, and personal data protection. He also often shares his tips and best practices in relation to internet security and digital safety of private individuals and small businesses, including some additional applications of using a VPN service.
Comments (1)
Guy, you’re to much. The article is so interesting and thoroughly explanatory. I enjoyed reading it.