Although most experts will agree that it is impossible to asses exactly what innovations will be made in the future, cybersecurity trends in 2019 have reinforced some patterns predicted in the last few years and introduced some new ones.
The most obvious overarching trend is the further regulation of the internet for the average user, with ever-increasing surveillance, data collection, and monitoring. While this spells major benefits for trade, security, and daily communication, it is also a risk to the freedom and liberty of users.
Thankfully, increased awareness about cyber-hygiene is slowing the diminishment of liberties and surveillance, leaving more time for privacy protection tools to catch up.
Currently, most internet users are aware of the benefits of using a VPN, and professional VPN providers like Le VPN are even introducing other tools that will not only disguise our IP address when browsing the internet but also protect our data and devices from any snooping and hacking.
What has Changed?
It is currently undisputable that the internet will be the future of not only business and trade, but design, manufacturing, and research as well.
The only significant thing that has changed is the general outlook of the users about their security on the internet. Single passwords have become the thing of the past, and an increasing number of people are using multiple types of verification.
Those knowledgeable about how most systems are hacked, are even using burner-phones solely for their passwords.
Finally, due to so many smartphones switching to biometrics, PIN codes and passwords are slowly being exchanged for fingerprints and retina scans.
While for some this indicates to the grim dystopian future of so many science fiction novels and shows, it is currently very good for business and cybersecurity as well.
Not as Grim as It Might Seem
Humans have a natural tendency to focus on the bad, and in the age of instant mass media, this has painted a picture of a grim and miserable future and present.
But, we are actually very far from that reality and getting further as we speak.
The interconnectivity of the people has made major strides in the protection and proliferation of liberty all over the world. By using VPN connections and strong P2P encryptions, we can circumvent most of the issues and focus on the good things.
But, as is the case with every year, there is the good, the bad, and the ugly when it comes to cybersecurity trends, and we must do our best to manage them the best way we can.
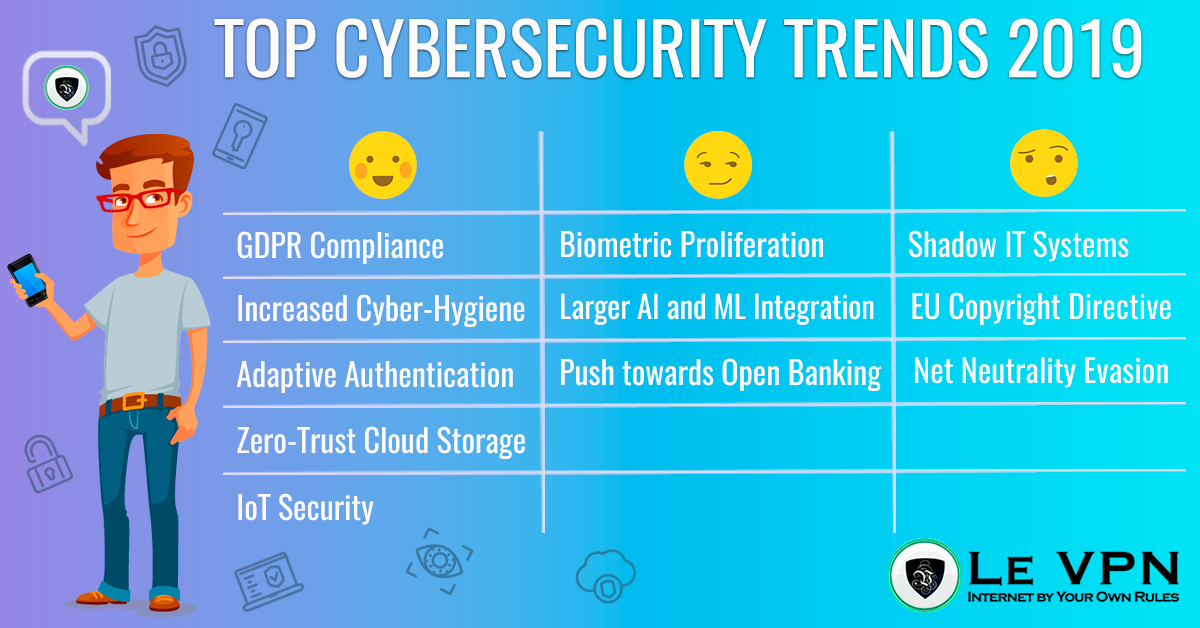
The Good
It’s always best to start with the good news.
Some critics say how we are yet to see major impacts of the GDPR and other EU laws, as no major companies have been affected by the legislation. But, for the time being, this legislation has proven to serve its intended purpose.
On top of the legal actions, industrial and personal behavior has also changed to focus more on cybersecurity as a means of prevention. Having protected devices and staying safe online is no longer an afterthought, but the primary concern of both companies and individuals.
Finally, our desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones are not the only focus of cybersecurity anymore. The Internet of Things, or IoT, has developed so much that we now need to think extensively about the security risks that might attack our ovens, refrigerators, and toasters.
GDPR Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, has fallen under a lot of criticism from its implementation in May of 2018 but has yet to show any major flaws in its functions.
Most significant data collectors globally haven’t had major issues with implementation, and the legislation has assisted users outside of the EU, such as those in the US, Canada, and Australia, to have their data protected.
It is yet to be seen how far this law would go in protecting the privacy of Europeans against large corporations, but it has at least given a bit of time for average users to get up to date with their cybersecurity and online privacy.
Increased Cyber-Hygiene
The term cyber-hygiene is rising in popularity when it comes to cybersecurity, as an increasing number of leaks and security breaches are made by human error and not a software failure.
This practice is especially important for home users, as they rely the most on software protecting their private data and reinforcing personal information security. This practice needs to become a part of your cyber security strategy.
Cyber-hygiene means you should leave your data around willy-nilly. Security should extend further than just passwords and security questions and should include addresses, phone numbers, and even personal names.
While there are no courses for cyber-hygiene, user-focused software such as Microsoft Office or even email security features will remind you not to share your data with entities you don’t trust.
Some people are even making fake profiles using burner phones and online cards when they want to collect coupons and benefits, which is a genius solution to create a real-life VPN, and is probably going to become a significant tool in fighting identity theft as well as ransomware.
This digital avatar would not only make you safe in countries where corporations snoop for your data, but would also allow you to circumvent any Google censorship in countries that have other issues.
Adaptive Authentication
Unlike most other trends visible today, adaptive authentication has only become prevalent in the last twelve months. Currently, it is taking cybersecurity experts, companies, and individuals by storm with new ideas and options.
The main feature of adaptive authentication is that risks are no longer seen as stationary and direct. Rather, we now know that hackers, snoopers, and other malicious entities online will adapt quite quickly to any loopholes present in the system.
This solution has become a part of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework that informs the private sector in the US how to defend themselves from online threats.
Because of this adaptability of the cybersecurity threats we face, trends indicate that we will see an advance in multi-factor authentication, including biometric verification.
The goal of AA is to forgo predicting the threat but giving the users tools capable of adapting to the cyberattacks and fighting off hackers ad hoc.
Zero-Trust Cloud Storage
Last several years have seen multiple hacks of services such as the cyber attacks on iCloud, or similar cloud storage systems that have led to thousands of people having their files, information, and even pictures illegally downloaded.
Thankfully, companies have come to their senses and changed their approach to cloud storage.
With the Zero-Trust Cloud storage, companies no longer directly allow users to access their data but monitor their behavior to determine if the device obtaining their information is the same one they regularly use.
If there is anything suspicious, the email and other devices of the user will be notified, giving them time to resolve the issue.
This is especially beneficial cloud security for people using a VPN. With companies like Le VPN, all of your devices can be connected to the same VPN server, normalizing your behavior from the app’s perspective.
If there is a breach of security and someone has obtained your access keys, the device they use will have a different IP address and be blocked from accessing your private data.
Focused on IoT Security
The New Year has seen an increased interest in IoT security, as more and more of our devices are becoming digitalized and connected to the internet.
This aims to remove vulnerabilities from products that do not contain enough processing speed to have their own dedicated cybersecurity systems. In these cases, it is important to have critical infrastructure developed that would protect these devices from the outside.
Alone, IoT products might create a cyber risk, but current trends in cybersecurity aim to push for more protection. This can be done by using a VPN router for your entire home, or serially connecting all of your IoT devices to a singular device that is protected by a VPN, firewalls, and anti-malware software.
Removing the security risk from the peripherals in our home will significantly reduce the number of attack vectors that hackers can use if they were to attack our privacy and personal data.
The Bad
There are always two sides to every coin. While the advancements we see in international trade and biometric data will be beneficial for individual safety, it will also become a risk for personal freedom, as well as job security.
The only thing we can do now is to be aware of the technology and to know which trends to watch.
Security measures have been in place to minimize the risk of artificial intelligence AI and machine learning being misused. But, we have all seen The Terminator, and are aware of some of the bleak scenarios that we can face if not careful.
Biometric Proliferation
Fingerprint verification has been around at our workplaces and smartphones for some time now, but have seen an explosion in the last several years. This influenced both network security as well as device security.
Currently, most modern smartphones have some sort of biometric verification, with either a visual or sonic fingerprint reader, facial recognition, or retina scanners.
For most people, this means that their phones and other devices are safer. Having your phone or tablet stolen now doesn’t spell all of your pictures and private data being taken for ransom by the thief.
But, the proliferation of biometric data has also given another attack vector to both hackers and countries that don’t value privacy as much.
In the last year, the People’s Republic of China has instituted a program of ‘’Social Credit’’ that follows the habits of its citizens using biometric data, punishing any behavior deemed an issue for national security, or even just unfit, with reduced life choices, such as buying plane tickets.
Finally, there is no way to hide your biometric data, as you would your IP address or phone number, which creates security challenges in regards to corporations and countries, rather than individual hackers.
Larger AI and ML Integration
While the significant advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are leading to the decrease of costs in goods and services, this industry shift is also seeing a decline in the number of jobs for people that formerly created those goods and services.
Self-driving cars are predicted to reduce trucking and taxi service jobs, and self-checkout machines are removing the need for tellers and salespeople. Retail jobs in shopping malls are steadily declining in favor of online shopping.
This is also an issue for cybersecurity as these services can be easily tracked and that data can be collected by corporations and stolen by hackers and other criminal elements.
Finally, while the reduction in employment doesn’t directly impact our cyber security, it can affect social changes that might impact our physical safety.
Push towards Open Banking
Similar to AI, Open Banking also reduces the cost of doing business on the global level while simultaneously opening an attack vector for device hacking and unauthorized data collection.
While this category of financial cybersecurity trends will probably benefit companies, as well as tech-savvy individuals, it might create a further social divide that will exclude those with lower incomes.
In both cases, it is unwise to use third-party services that might not be stationed in your country to make financial transactions, at least from your primary account. Users will need to be aware of the risk before using the benefits of open banking.
The Ugly
Finally, some cybersecurity trends for 2019 are just plain ugly. These include either daft and unreasonable legislation that is detrimental to both cybersecurity and the economy, or mistakes that were made in the past that are just now coming to life.
In most cases, they are the product of misunderstanding about how the worldwide network works. But, sometimes it is the users that have made their own mess by not keeping their security systems up to date.
Shadow IT Systems
Regretfully, the advance of modern devices is so fast that most of them become forgotten in the piles of used stuff. Before, this would be considered just junk, but if these devices can be connected to the internet, they can create a shadow network that is invisible to modern cybersecurity protocols. This issue with information technology security was predicted, but didn’t show any signs of volition until the last few years.
This doesn’t include solutions like the FSB (formerly known as KGB) using analog typewriters for sensitive data, or homeland security using outdated peripherals, as this cannot influence other devices.
Personal risks include using a smartphone from six or seven years ago to access the internet. As these devices are no longer supported, you will not be safe. Also, there is a question of legacy apps, which have obsolete application security, being misused or even dismantled to serve as malicious software.
Article 13 Evaluation
Popularly known as Article 13, this refers to an article of the EU Copyright Directive. Although the disturbing part has been moved to Article 15 now, it still has the same content as before.
Most critics explained the worst case scenario for the implementation of this directive, which might even go so far to have state-wide (or even EU-wide) copyright filters.
The more moderate standpoint is that this directive is more or less mute, proposing less copyright security than what is already in place for most EU countries, or the US as the main origin of most content.
By reading it word for word, the only thing Article 15 might impact is the removal of links from media compilations.
This directive is much less invasive than some software that is already in place, such as the YouTube copyright algorithm.
Net Neutrality Evasion
Fears of most Americans came true when several companies announced that they might charge more for fast internet access to some services that are owned by their competitors.
As the US already lags behind most of the Planet with their internet speed, with mobile speeds being behind countries like Turkey, Oman, or North Macedonia, this reduction in internet speed might even further impact users.
While the short-term solution here can be using a VPN to override this reduction, it is possible that the dissolution of Net Neutrality might impact even VPN providers in the future.
How to Protect Yourself?
Aside from recommendations that were already present, like always connecting over a VPN, as well as keeping your anti-virus and security software up to date, and increasing emphasis is being made on cyber-hygiene and IRL anonymity.
The wisest thing for users to do is to have as many layers between them and any snoopers as they can. This can include using multiple servers with virtual private networks, different identities online, and even making purchases with a pseudonym rather than with their real info.
VPN & More
It is not enough for a VPN just to conceal your IP address anymore. Premium VPN providers need to use some sort of P2P encryption and to secure all of your devices as well as your primary one.
Finally, expat VPN use is the best way you can use the same cybersecurity infrastructure wherever you go, concealing your digital footprint and ensuring your data security.
Conclusion
Although the media would like to portray cybersecurity trends for 2019 as a bleak picture, this is just due to human psychology. The bad parts on the horizon are mostly theoretical while the good aspects are proven.
If you want to stay safe online, as well as to protect your personal information and private data, the best way to do this is to use a VPN. Premium VPN companies like Le VPN have extended their services far beyond just global servers, and now include P2P encryptions, modern safety protocols, as well as other perks.
With a VPN as the basis of your cybersecurity framework, a bit of knowledge and by just using common sense, you can be safe and use everything the internet has to offer.
SUMMER SALE
First 3 years for $2.22/mo
NO LOGS
100+ LOCATIONS
P2P ALLOWED
Easy To Use
30-Day Money Back
Friendly Support
Bitcoin Accepted
Ultra High Speeds



Written by Vuk Mujović @VukMujovic
Vuk Mujović is the founder of MacTíre Consulting, an analyst, data management expert, and a long-term writer on all things business & tech. He authored blogs, articles, and opinion pieces aimed to help both companies and individuals achieve growth without compromising their security. Vuk is a regular guest author to Le VPN Blog since January 2018, where he gives his expert opinion on the topics related to cybersecurity, privacy, online freedom, and personal data protection. He also often shares his tips and best practices in relation to internet security and digital safety of private individuals and small businesses, including some additional applications of using a VPN service.